
Trends in the Cost of Employer-Sponsored Coverage
Data Bulletin No. 14
Fall 1998
M. Susan Marquis, Stephen H. Long
Cost of Employer-Sponsored Insurance
| Site | Average 1-Year Change |
| Orange County, Calif. | 0.2% |
| Cleveland, Ohio | 1.1 |
| Miami, Fla. | 1.1 |
| Boston, Mass. | 1.6 |
| Phoenix, Ariz. | 1.8 |
| Lansing, Mich. | 2.0 |
| Syracuse, N.Y. | 2.1 |
| Seattle, Wash. | 2.4 |
| Indianapolis, Ind. | 2.6 |
| Newark, N.J. | 3.0 |
| Greenville, S.C. | 3.3 |
| Little Rock, Ark. | 3.8 |
| United States | 1.9 |
| Employer-reported premium increases weighted by employer size. None of the site changes are significantly different from the U.S. mean at the p<0.05 level. 1997 RWJF Employer Health Insurance Survey | |
![]() ncreases in the cost of employer-sponsored health insurance have been quite moderate in recent years, in contrast to the double-digit growth rates in the late 1980s and early 1990s. In 1997, premiums increased on average only 1.9 percent over the previous year, according to employers that participated in the 1997 Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (RWJF) Employer Health Insurance Survey. Other recent employer surveys also report moderate cost increases nationwide for 1997 and 1998.
ncreases in the cost of employer-sponsored health insurance have been quite moderate in recent years, in contrast to the double-digit growth rates in the late 1980s and early 1990s. In 1997, premiums increased on average only 1.9 percent over the previous year, according to employers that participated in the 1997 Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (RWJF) Employer Health Insurance Survey. Other recent employer surveys also report moderate cost increases nationwide for 1997 and 1998.
Variation by community was modest, and there was only a 3.6 percentage point difference in cost increases among the 12 randomly selected sites in the Community Tracking Study, with a low of 0.2 percent in Orange County and a high of 3.8 percent in Little Rock.
Distribution of Cost Changes Among Employers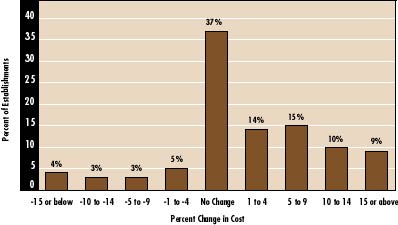 1997 RWJF Employer Health Insurance Survey |
![]() espite the low level of cost increase overall and modest variation among communities, there was substantial variation in cost changes among employers. Thirty-seven percent of employers that offer health insurance reported no change in their 1997 costs (see graph). But 19 percent of employers offering insurance reported that the cost of their plans in 1997 was more than 10 percent higher than the previous year, and 7 percent reported that the cost of providing coverage fell by more than 10 percent.
espite the low level of cost increase overall and modest variation among communities, there was substantial variation in cost changes among employers. Thirty-seven percent of employers that offer health insurance reported no change in their 1997 costs (see graph). But 19 percent of employers offering insurance reported that the cost of their plans in 1997 was more than 10 percent higher than the previous year, and 7 percent reported that the cost of providing coverage fell by more than 10 percent.
Small employers experienced greater variation in premium changes than large employers. Thirty-four percent of firms with fewer than 10 employees reported changes in excess of 10 percent: 26 percent reported increases and the remaining 8 percent reported decreases. Among employers with 100 or more employees, reports of changes exceeding 10 percent in either direction were only about half as common (19 percent) as in small businesses.
Changes in Premiums in Excess of 10 Percent by Firm Size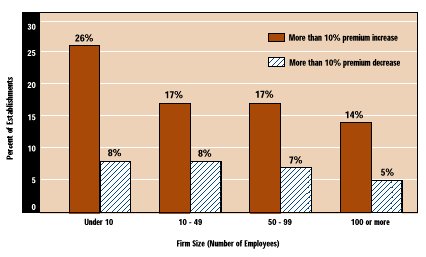 1997 RWJF Employer Health Insurance Survey |
COST ISSUES TO CONSIDER
![]() he extent to which the moderate cost growth documented here reflects efforts by employers to contain costs, as distinct from other causes, requires further investigation. For example, the reported changes in premiums do not account for factors that may contribute to the small increase in costs, such as changes in benefit design, the types of plans offered by employers and the types of plans chosen by employees.
he extent to which the moderate cost growth documented here reflects efforts by employers to contain costs, as distinct from other causes, requires further investigation. For example, the reported changes in premiums do not account for factors that may contribute to the small increase in costs, such as changes in benefit design, the types of plans offered by employers and the types of plans chosen by employees.
Moreover, the modest overall growth masks substantial increases in the costs faced by some individual employers, especially small firms. If these increases lead to employers’ dropping insurance as a benefit or increasing what employees pay, employees in these firms may have less access to health insurance.
This Data Bulletin presents results from the 1997 Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Employer Health Insurance Survey, a nationally representative telephone survey of private and public employers. It is based on responses of 21,543 private establishments. The survey is a component of Health System Change’s (HSC’s) Community Tracking Study. It was conducted by Research Triangle Institute (RTI) and designed by RAND and RTI, with collaboration from HSC.